The Role of Data Analytics in Healthcare
Topics
- Unlocking the power and promise of healthcare data to drive transformation
- What is data analytics in healthcare?
- Six benefits of healthcare analytics
- Three primary types of healthcare data
- What are the types of analytics in healthcare?
- Applications of analytics in healthcare
- Building an effective analytics
- Making data actionable and improving outcomes with predictive analytics
- Setting a strong foundation for better healthcare
- The future of analytics in healthcare
Unlocking the power and promise of healthcare data to drive transformation
The tremendous advancement of healthcare data analytics in the last decade has led to much disruption and innovation across healthcare. Today, with the rapid speed and accuracy of data analytics, hospitals, clinicians, patients, vendors, manufacturers, and others are able to share and receive critical information faster and more seamlessly. Having timely access to relevant healthcare data is a game changer that is driving greater connectivity and efficiency while improving patient outcomes and reducing costs to name just a few benefits.
But what exactly is healthcare data analytics and how can it help healthcare organizations improve clinical, operational, and financial performance? Below, we explore these questions with a look at how healthcare organizations are harnessing the power of data analytics across the healthcare ecosystem.
What is data analytics in healthcare?
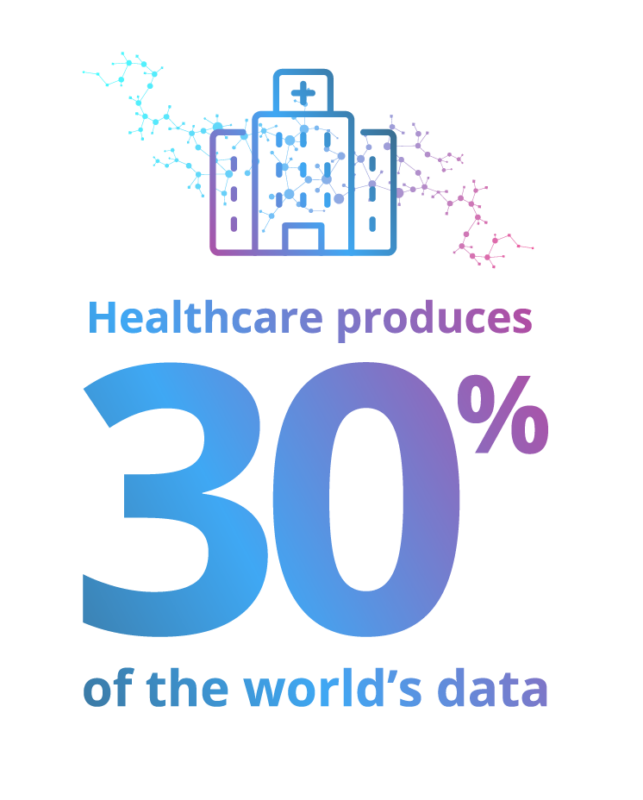
While this is good news for hospitals and other organizations looking to improve patient care and safety and allocate resources more efficiently, adding further complication is the significant amount of digital information still buried in data silos. Healthcare faces the steep challenge of unlocking, ingesting, analyzing, and using this data more effectively.
This is where the power of healthcare data analytics comes in.
An article in the journal Health Services Research and Managerial Epidemiology defines healthcare data analytics as “…a study of methods and techniques to analyze data, discover new information and knowledge, link data in terms of its semantics, and describe data to other informaticians, managers, and other stakeholders.” More simply put, the goal of healthcare data analytics is to pull data from disparate sources and organize it into a cohesive, cloud-based system, making it available to end users in usable formats. Healthcare data analytics is integral to virtually every aspect of healthcare. For Example, using data analytics:
- Physicians can receive real-time patient care insights and alerts via the EMR at the point of care to target and treat high-risk conditions
- Patients’ can access personalized information more readily, including health records, lab tests, and billing
- Hospital revenue integrity departments can predict claims errors and identify missing revenue
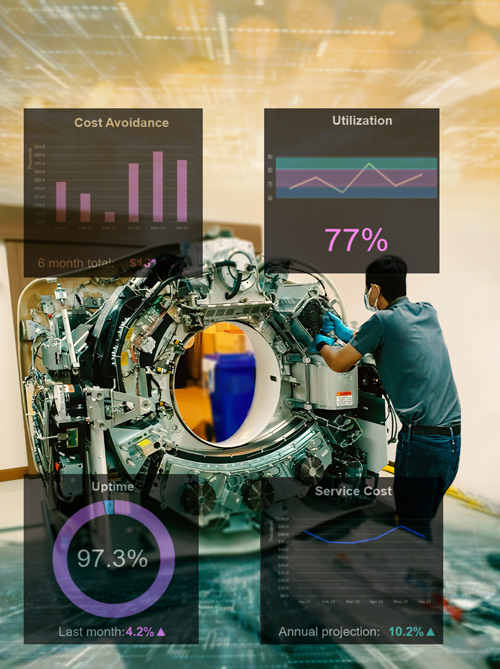
- Hospitals can receive real-time data from connected machines, such as CTs and MRIs, to optimize service and utilization and improve uptime
- Facilities can proactively manage building equipment such as boilers and HVAC units to prevent costly breakdowns
Six benefits of healthcare analytics
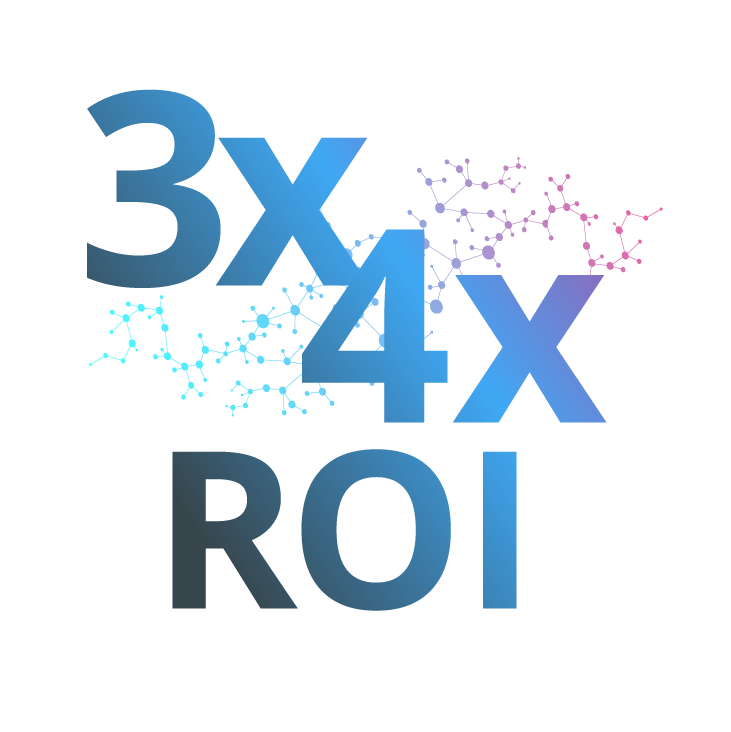
Organizations can also tap into the power of data mining for insights that aren’t intuitive on an individual level to do things such as comb medical records to find and eliminate clinical care gaps; scrub clinical documentation to reduce denials; and look at machine and device data to manage service requirements. A robust data analytics solution can quickly pay for itself with a 3X-4X ROI in hard and soft benefits, including the following:
- Raises organizational intelligence
- Drives greater collaboration and efficiency
- Boosts patient safety, care quality, and care outcomes
- Increases proactive decision-making
- Optimizes utilization of fixed assets/increases ROI
- Reduces costs/improves margins
Three primary types of healthcare data
In healthcare, data analytics is used to capture, ingest, and convert three types of data:
- Structured data: A vast amount of structured (understandable) data sits in data silos that are difficult to access and share. This data typically resides in transactional legacy systems, such as electronic medical records (EMRs), picture archiving and communications systems (PACS), and radiology information systems (RIS), and others.
- Unstructured data: Connected machines and buildings create a large quantity of data that is used by healthcare providers, original equipment manufacturers (OEMs), software companies, and others. Much of this data is unstructured, meaning, it’s free flowing information that cannot be readily understood. It must be captured and converted into usable information.
- Patient data: Patients are generating increasing amounts of data through smart phones and mobile apps. Most of this data resides in different silos either in clouds or via on-premises solutions.
What are the types of analytics in healthcare?
Through analytics, healthcare organizations have an opportunity to look more deeply at the data, drilling down to specific insights. The following are four types of analytics typically used in healthcare.
- Descriptive analytics looks at historical data and patterns, enabling organizations to quickly connect the dots to make daily and weekly decisions. Descriptive analytics us used in simple reports, charts, and graphs and is often referred to as the low hanging fruit. Descriptive analytics is a good starting point for organizations new to data analytics.
- Predictive (proactive) analytics applies algorithms and machine learning techniques to data to make future predictions in certain areas such as hospital bed capacity, patient adverse events, patient scheduling needs, and maintenance requirements on clinical assets. Applying data science at this level enables healthcare organizations to be more proactive in their decisions.
- Prescriptive analytics captures larger amounts of data, providing actionable insights and informing future strategies.
- Learning from user experiences is the newest frontier in healthcare data analytics. Healthcare organizations are now able to crowdsource and learn from user interaction data, including patient ratings. Over time, an organization becomes smarter as it starts to learn what patients and consumers like and don’t like.
Applications of analytics in healthcare
Having a strong data analytics platform is essential for all healthcare organizations, and especially those looking to move into smart hospital territory. A comprehensive data analytics solution will enable organizations to ingest and scrub data for insights from three primary areas that are typically challenged by data silos:
 1. Healthcare professionals and patients
1. Healthcare professionals and patients
Dynamic scheduling models: Using data analytics, hospitals and medical practices can predict future scheduling needs and share scheduling information to optimize facility and clinician capacity. Real-time information enables them to book patient appointments with the right provider at the right facility at the right point in time instead of moving the appointment further out. Maximizing scheduling capacity improves patient access and care quality, ROI for fixed assets such as medical equipment, and ultimately revenue.
 2. Healthcare machines
2. Healthcare machines
Maximizing efficiency and utilization while reducing service costs: Without data analytics many healthcare organizations fly blind when it comes to managing fixed assets such as connected machines, including CT scanners and MRIs. For Example, healthcare data analytics can help organizations avoid an expensive service contract with the original equipment manufacturer (OEM). Analytics also provides key utilization information by facility and OEM type to ensure clinical assets are running at full capacity, while also identifying causes of underutilization such as scheduling or workflow issues.
And predictive intelligence can identify maintenance issues and when a particular piece of equipment is going to fail long before it goes out of service, allowing preventive maintenance and less downtime. Moreover, combining equipment data with real-time locating systems (RTSL) enables organizations to make meaningful decisions. All of this adds up to a richer ROI.
 3. Healthcare facilities
3. Healthcare facilities
Building automation: As smart hospital technology takes off, organizations are creating data frameworks to integrate medical device data with building automation systems.
Building an effective analytics strategy
Managing large amounts of healthcare data against a maze of complicated government legislation and regulations—that oversee patient safety, care quality, security, and privacy—requires tight strategic oversight. Successful healthcare organizations recognize that establishing a framework for a data-driven enterprise is a critical step to ensuring regulatory compliance and improving the following:
- Patient quality care
- Patient safety
- Patient outcomes
- ROI on fixed assets
- Organizational margins
According to a McKinsey report, data-driven enterprises of the near future will share the following seven key components:
- Data will be central to every process and decision
- All data will be in real-time
- Flexible organizations will use a variety of data bases types
- Data assets will be treated like products with product teams
- The chief data officer will head up a business unit with profit-and-loss responsibilities
- Data silos will be replaced by broad data sharing relationships
- Data management will prioritize automated privacy and security
Explore the Possibilities
With more than 5 million exams analyzed annually by Glassbeam solutions, see how top organizations are transforming their log data into impactful insights.
Making data actionable and improving outcomes with predictive analytics
Relying purely on historical data to solve healthcare problems keeps organizations in a reactive stance and leads to a continuous loop of stagnation. Applying new rules and algorithms to problems, however, results in prescriptive, actionable solutions. With the right data analytics strategy, healthcare organizations can ingest and combine different data sources to reveal predictive insights.
For Example, a health system looking to optimize utilization for a fleet of CT machines and other fixed assets can apply predictive analytics to determine the best time to procure parts, rather than being reactive and replacing them immediately. The former ties up less capital and takes advantage of just-in-time inventory principles. As organizations following this path continue to collect more data, they will start to make more predictions, benchmark results, and develop best practice data analysis. Ultimately, these actions will drive greater efficiency, cost savings, and a more proactive mindset.
Setting a strong foundation for better healthcare
As the healthcare industry continues to experience disruption from COVID-19, staffing shortages, and rising costs, hospitals and other organizations are finding they must become more resilient and culturally competent. Big data analytics can help by providing organizations with more targeted, in-depth data, analysis and actionable insights as they pursue key goals aimed at keeping patients safe, prioritizing value-based care, building stronger talent pipelines, making a digital transformation, and cutting costs. With a strong data foundation, hospitals have a more complete vision of their organization and how they fit within the healthcare landscape.
The future of analytics in healthcare
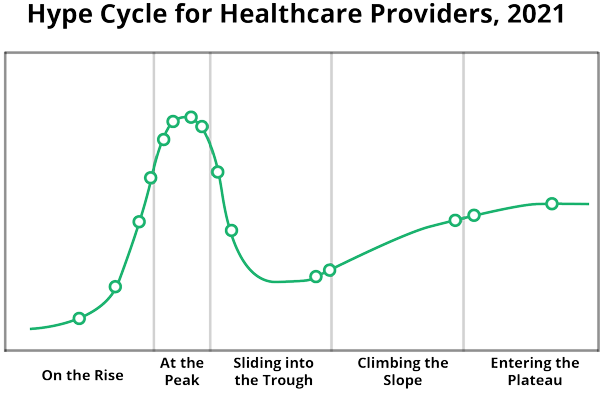
How far are we on the data analytics-digital transformation continuum? According to Gartner’s “Hype Cycle for Healthcare Providers,” healthcare analytics architecture for providers is 5-10 years out. Most would agree there is still much untapped potential for data analytics over the next decade. However, healthcare organizations still saddled with legacy systems that were not built to talk to one another will need to solve interoperability challenges and invest in a single unified data platform and data analytics solutions that can move raw data into usable insights.
Advances in healthcare data analytics are predicted to lead to a smart hospital transformation in the healthcare industry. Hospitals are already starting to make existing facilities smarter by creating a digital framework consisting of a command center network, a data infrastructure, and an EMR. Investments made today in healthcare data analytics will give organizations a stronger competitive edge in the near future.
Transform Your Healthcare Operations
See how to gain deeper, clearer insight from your machine data to elevate business intelligence and to improve your operational uptime, utilization, and efficiency.
 1. Healthcare professionals and patients
1. Healthcare professionals and patients 2. Healthcare machines
2. Healthcare machines 3. Healthcare facilities
3. Healthcare facilities